What is the GPCI?
Given the global competition between cities, the Global Power City Index (GPCI) evaluates and ranks the major cities of the world according to their “magnetism,” or their comprehensive power to attract people, capital, and enterprises from around the world. It does so through measuring 6 functions—Economy, Research and Development, Cultural Interaction, Livability, Environment, and Accessibility—providing a multidimensional ranking. The GPCI is able to grasp the strengths, weaknesses, and challenges of global cities in a continuously changing world not only through a ranking, but also through analyzing that ranking’s specific components.
Download the latest GPCI-2020 report
Target Cities
Executive Summary
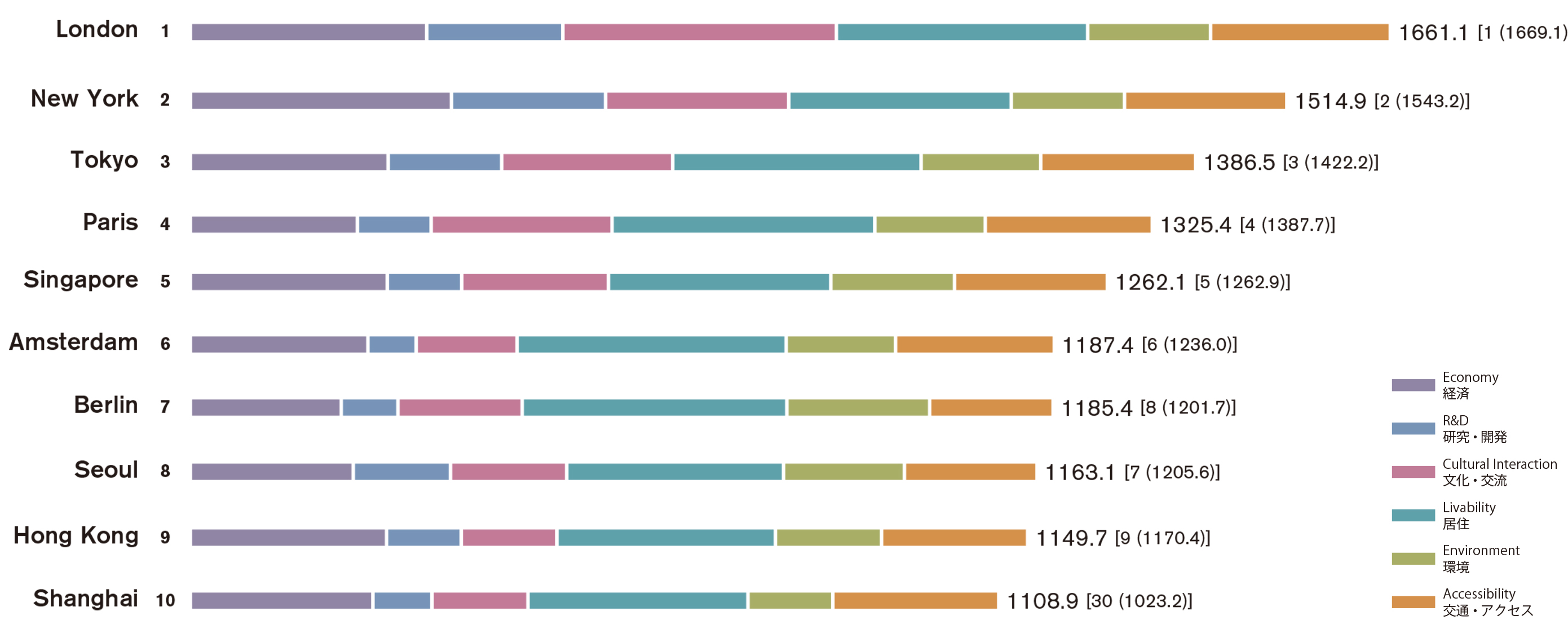
Top 10 Cities
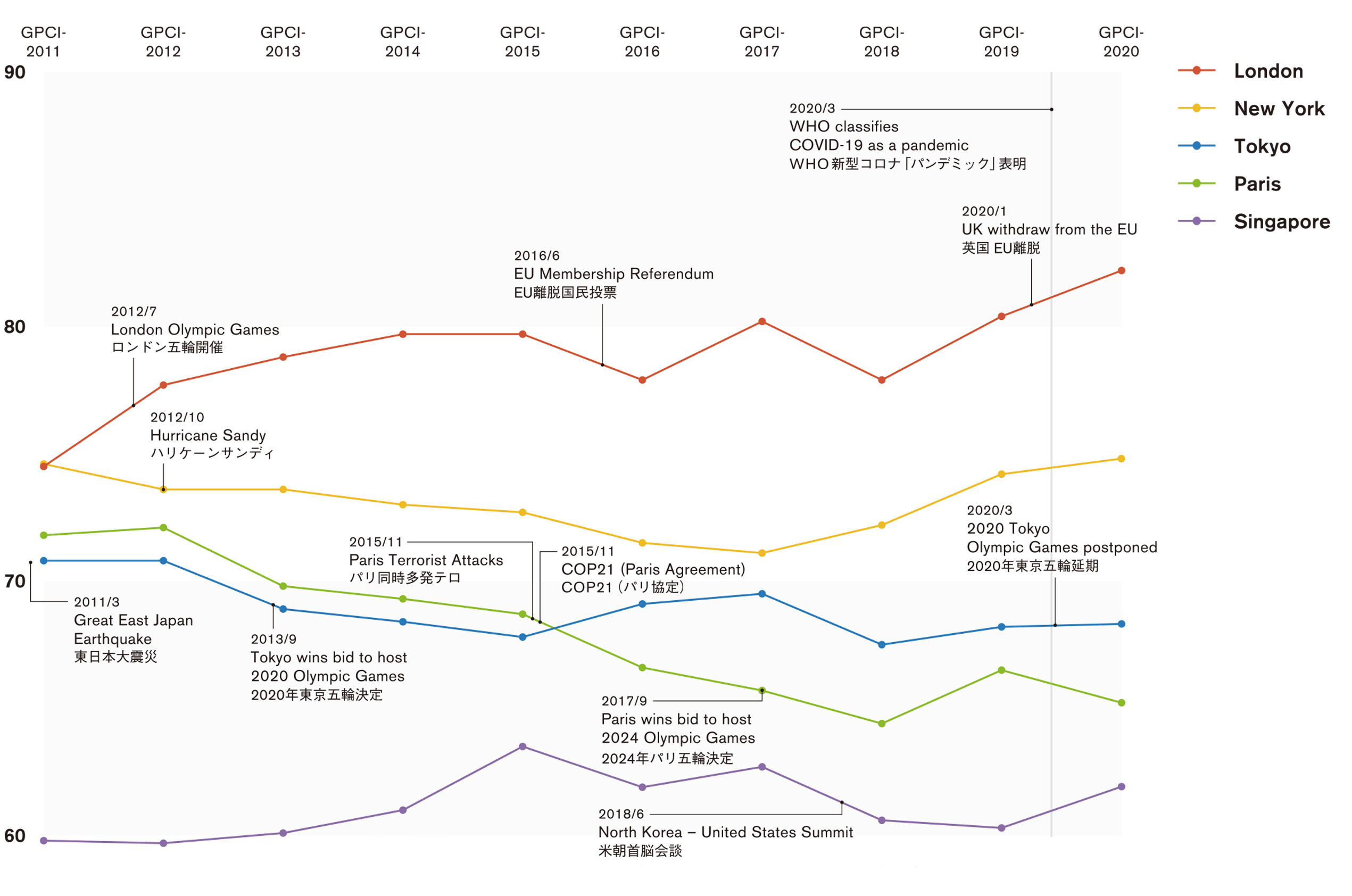
Although the 3 top-ranking cities kept their positions from last year, when comparing the fluctuation in deviation scores, London (#1) and New York (#2) were seen to pull away from Tokyo and Paris. Berlin (#7) increases its scores in Economy, Livability, and Environment, taking Seoul’s position from last year. Shanghai was the only new entrant into the top 10 cities as it improved its scores across 5 functions, rising dramatically in its ranking.

This year’s results saw London maintain its first-place position for the 9th consecutive year, while creating a large distance between other cities in terms of deviation score. Aside from Environment, London is placed in the top 10 for all functions, and is especially strong in Accessibility where in addition to holding on to the top spot in two indicators, the city also improved its score from last year in four indicators, ranking first in Accessibility. Despite the gap between #2 New York extending further in Economy, London boasts a stable comprehensive strength at the top of Cultural Interaction.

New York was once again dominant in Economy this year, increasing its scores in Total Employment and Employees in Business Support Services, as well as reaching #1 in Variety of Workplace Options. Though the city maintained its top ranks in Research & Development and Cultural Interaction, its scores in Ease of Mobility by Taxi or Bicycle and Traffic Congestion fell, causing it to hand over the #3 position in Accessibility to Shanghai.

Preserving its #3 rank, Tokyo continued to display its consistent strengths in all functions while also raising its rank in Environment and Accessibility. Due to a drop in scores for Workstyle Flexibility and Social Freedom and Equality, Livability was the only function where the city’s rank fell. In Research and Development, in which Tokyo maintained a #3 position, the city’s rank in Academic Performance fell, though it was able to obtain a high ranking in Number of Startups.
Reports

GPCI-2020 SUMMARY
"Global Power City Index 2020 Summary" includes the details of Comprehensive Ranking and Function-Specific Ranking, list of indicators and definitions, Actor Evaluation.

GPCI-2020 YEARBOOK
Release Date: 15 January, 2021
Bilingual (Japanese and English)
Print Edition: JPY 20,350 (tax included)
PDF: JPY 16,500 (tax included)
The Global Power City Index YEARBOOK 2020 is a full report of the GPCI-2020, providing a detailed account of its methodology and results. The city profiles analyze each of the 48 target cities of the GPCI and illustrate the city’s strengths and weaknesses in reference to the score and ranking of the 70 indicators. The detailed definitions and sources of the indicators are also included in the book.
Press Resources
- GPCI 2025
- GPCI 2024
- GPCI 2023
- GPCI 2022
- GPCI 2021
- GPCI 2020
- GPCI 2019
- GPCI 2018
- GPCI 2017
- GPCI 2016
- GPCI 2015
Contact
If you have any questions about the Global Power City Index, please contact iusall@mori-m-foundation.or.jp
PUBLICATIONS
For more information about the Global Power City Index, please see the Summary or order the YEARBOOK. You can download the PDF version of the Summary below. The YEARBOOK provides specific details on the methods of research, definition of indicators, lists of data sources, and scores and ranking analysis of each city.